-40%
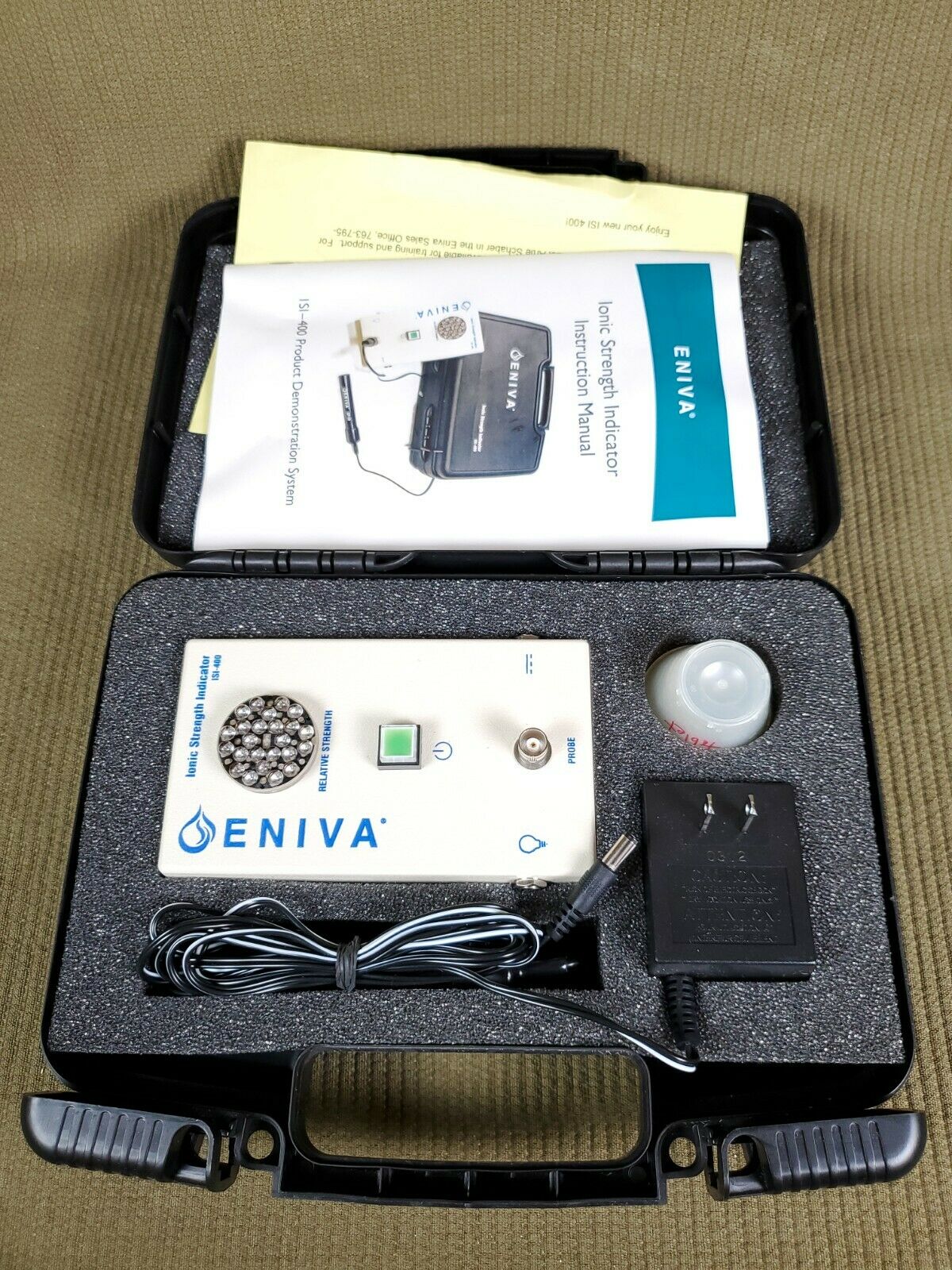
Precise Eniva Ionic Strength Indicator ISI-400 with LED Display
$ 180.57
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Nice Condition as seen images.Questions Always Welcome.
Thanks For Looking
MFG Info
The concept of ionic strength was first introduced by Lewis and Randall in 1921 while describing the activity coefficients of strong electrolytes. The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in that solution. Ionic compounds, when dissolved in water, dissociate into ions. The total electrolyte concentration in solution will affect important properties such as the dissociation constant or the solubility of different salts. One of the main characteristics of a solution with dissolved ions is the ionic strength. Ionic strength can be molar (mol/L) or molal (mol/kg water) and to avoid confusion the units should be stated explicitly.
The product Eniva Ionic Strength Indicator ISI-400 is with LED Display, CP-10 Test Probe, Low-Voltage Power Supply, Protective Carrying Case, Plastic Measuring Containers and Instruction Manual. The Eniva ISI-400 is a conductivity apparatus used to determine whether a solution can conduct an electric current. The ISI-400 along with the CP-10 conductivity probe (included) measures the ability of a solution to conduct an electric current between two graphite electrodes. The higher the ionic strength of a solution, the stronger the current. the stronger the current, the brighter the illumination level of the Relative Strength LED indicator.
There are some researches about Ionic Strength. Here is the abstract about the essay Relationship Between Ionic Strength and Electrical Conductivity for Soil Solutions: Activity of an element is a better predictor of plant growth response than its concentration. Ionic strength of the soil solution is an important property that is required to calculate ionic activity. Since its calculation requires measurement of all major cations and anions in solution, an alternative approach was sought to estimate it on the basis of a single measured property of solution. Griffin and Jurinak reported a linear relationship between ionic strength and electrical conductivity which was employed to predict ionic strength using soil solution samples from a wide range of soils subjected to varying treatments with respect to source of amendment, concentration of supporting solution, soil moisture content, and duration of incubation. This study has shown a very close agreement between ionic strength predicted using the Griffin-Jurinak relationship and the ionic strength calculated using concentration and valence values for all cations and anions in solutions. Furthermore, for the conditions of soil solutions from variable charge soils, the Griffin-Jurinak relationship was modified.
More information: The effect of ionic strength studied at various NaCl concentrations in the anode chamber showed that our MFC system performed better when 10 mM NaCl was used. An average maximum power density of 12.8 mW/m2 and a corresponding current density of 35.5 mA/m2 were observed. When no salt was added in the medium, the increase in voltage was relatively insignificant. The voltage increased gradually when salt was added to the medium irrespective of the salt concentration. However, a maximum voltage of 0.338 V was generated in case of 10 mM. Corresponding current profiles showed that very low current was seen in the absence of the salt whereas the current generation slowly increased along with time on supplementation of NaCl to the medium. Addition of the salt increases the conductivity of the medium by decreasing the internal resistance of the solutions.